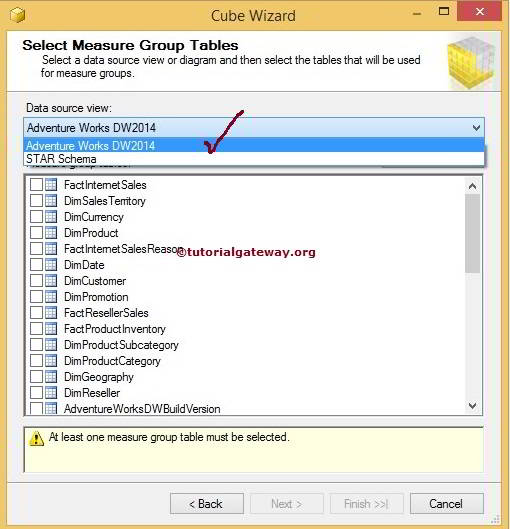
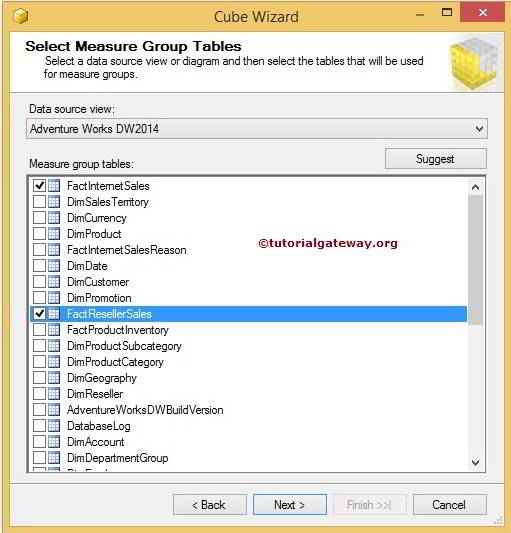
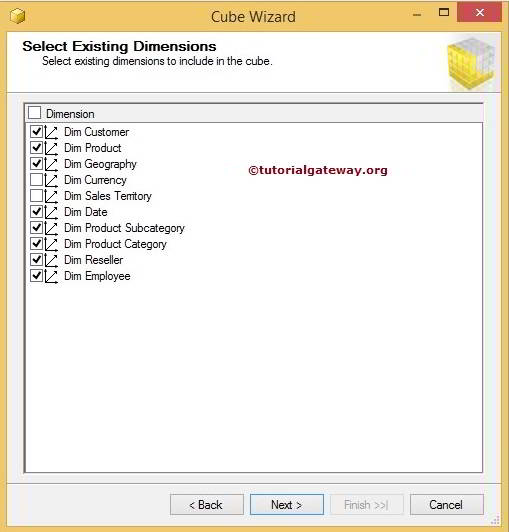
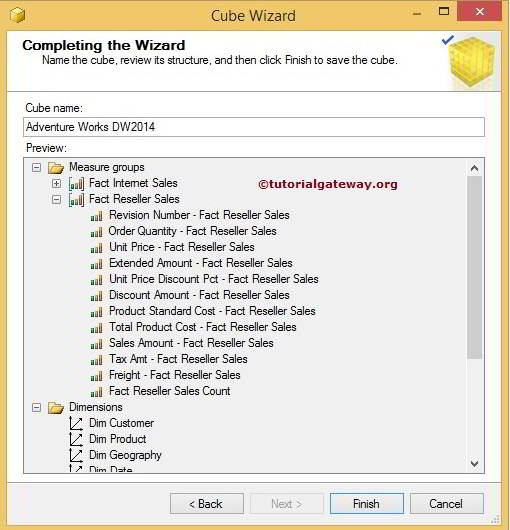
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 or 2K5 was released in the month of November, 2010. In SSRS 2005, virtual directories were created for Report Server and Report Manager. With the feedback from SSRS 2K5 users, Microsoft launched SSRS 2008 version with a lot of enhancements in its architecture, in the month of April, 2010. Out of all the enhancements made in its architecture, the major enhancement is making SSRS independent of IIS (Internet Information Services) which makes it easier to configure. Now, it uses HTTP Listener (HTTP.SYS) which helps to reduce the attack surface of the Report server. It doesn’t require any special setup to install as SSRS comes as an install option with Microsoft SQL Server Developer, Standard and Enterprise editions.
SSRS Architecture :- The full Reporting Services architecture includes development tools, administration tools, and report viewers. It can be summarized as a 3 Tier Architecture as shown below:- 

Tier 1:- Presentation Tier
Client applications and Built in/Custom tools constitutes the Presentation tier. The Presentation tier works on the data provided by middle tier and handles report generation and report visualization. It includes various components such as Report builder, Report designer, Model designer, Reporting services configuration and other Third party tools. Report generated can be visualized and administered by a Web browser.
Tier 2:- Middle Tier
This acts as a brain for Reporting services and known as Report server. Report server consists of various windows service components and web service components which interacts with Data tier components (Report server database and data sources). This constitutes the Middle tier.
1. Windows service components:-
- Programmatic Interfaces is responsible to handle on-demand reports, interactive report processing.
2. Web service components:-
- Scheduling and Delivery processor helps to deliver reports to the target destinations which are being triggered from a schedule.
- Delivery Extension is used to deliver reports to the specified locations either by an e-mail delivery extension or by a file share delivery extension. E-mail delivery extension uses SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) to send an e-mail message to the users whereas file share delivery extension saves the reports to a shared location on the network. Delivery extension works in conjunction with Report Subscriptions.
3. Components common to Window and Web service:-
| Extension Name | Task Performed |
| Security Extension |
|
| Report Processing Extension |
|
| Rendering Extension |
|
| Data Processing Extension |
|
Tier 3 – Data Tier
- Report Server Database.
- Data Sources like XML, Oracle, etc.
NOTE: – A Report server requires at least one Security extension, Data processing extension, and Rendering extension. Delivery and custom Report processing extensions are optional, but necessary if you want to support report distribution or custom controls.
- Report Server is the core engine and interacts with Report server Database. It provides services for implementation and delivery of reports.
- Report Manager is administered via Web browser and manages the Report Server. It provides front end access to the report server web service components
- Report Designer is a developer tool for creating reports.
- Report Builder is a simplified tool for business users to build reports on fly. It acts as a base for report creation with Report model.
- Report Server database stores report definitions.
NOTE: – RDL stands for Report Definition Language. It is an XML file and stores Query information, Data source information, etc.
With this we complete our post on SSRS Architecture. I hope you like it. Your comments and feedbacks are welcome below.
2- Report Processor:
When a report is send from the presentation layer, it will reach to the programmatic layer. Programmatic layer will initialize the Report Processor. Report processor will retrieve the report definition or model information then combines layout information with the data from data processing extension and renders it in the requested format.
Authentication, Report Processing, Rendering , Data Processing and Delivery Extensions
The report server supports five types of extensions, authentication extensions, report processing extensions, rendering extensions, data processing extensions and delivery extensions. A report server requires at least one authentication extension, rendering extension and data processing extension. Delivery and custom report processing extensions are optional.
Tier 1 (Data Layer)
Reporting Services is one of the core component of MS SQL Server. Reporting Services is a server based reporting platform that provides reporting functionality to the user.Report Server is central component of Reporting Services. In this article we will try to understand how SSRS works in native mode deployment.
Reporting Services Report Server runs in one of two deployment modes:
1. Native Mode
2. Sharepoint Mode
You can’t switch Report Server mode from one to another so user has to decide in which mode Reporting Services should be configured at the time of Reporting Services installation. Native mode is the default mode for Report server.
In Native mode Report Server is a stand alone application server that provides all viewing, processing and delivering of the reports and report model. Report Server is implemented as a Microsoft Windows Service called as Report Server.
Native mode reporting services Report Server 3 tier architecture is given below.
Report Server consists of a pair of Processing Engines and five special purposes of extensions which handle Authentication, Report Processing, Rendering, Data Processing and Delivery operation.
Let’s discuss each component from the above architecture.
Tier 3 (Client Application in Presentation layer)
User sends request to report server for Report Processing, Report Scheduling and Delivery etc from any of the client application present in presentation layer i.e Report Manager, Report Builder, Report Designer.
Tier 2 (Report Server Components)
1- Programmatic Interface:
Programmatic interface process all the requests sent to Report Server from the client application present in presentation layer. This includes requests from Report manager, Scheduling and Delivery Processor, Report Design Tools and Third party Tools. Programmatic Interface uses Internet Information Services (IIS) to receive the requests.
When a request arrives at the report server in the form of SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) and http request; Programmatic Interface interacts with the Report Server database in response to the request. When a report is requested the programmatic Interface initialize the Report Processor and when a Report Scheduling and Delivery is requested the programmatic Interface initialize the Scheduling and Delivery Processor.
2- Report Processor:
When a report is send from the presentation layer, it will reach to the programmatic layer. Programmatic layer will initialize the Report Processor. Report processor will retrieve the report definition or model information then combines layout information with the data from data processing extension and renders it in the requested format.
Authentication, Report Processing, Rendering , Data Processing and Delivery Extensions
The report server supports five types of extensions, authentication extensions, report processing extensions, rendering extensions, data processing extensions and delivery extensions. A report server requires at least one authentication extension, rendering extension and data processing extension. Delivery and custom report processing extensions are optional.
The Scheduling and Delivery Processor processes reports triggered from a schedule, and delivers reports to target destinations.
Tier 1 (Data Layer)
1- Report Server Database:
Reporting Server Database is a SQL Server database. This is created at the time of Reporting Services configuration. It stores Reporting Services data such as Report Definitions, Report Metadata, Cached Reports and snapshots. It also stored security settings, encrypted data, scheduling -delivering and extension information and folder hierarchy. This data is accessed through Report Server. Report Server Database can provide internal storage information for a single reporting services or multiple report server.
2- Data Sources:
This is the data which user wants to represent in reports.